形態學運算(Morphological Operations)
形態學運算主要應用於二值影像,用來分析與處理影像中物件的形狀、結構與分布。相關功能集中於 Process > Binary > ...子選單中。
基本操作
-
Make Binary 建立二值圖: 將影像轉換成黑白(0/255)圖像。預設會根據選取區域或整張影像的直方圖,自動決定閾值。若已設定閾值(
Image > Adjust > Threshold),將會跳出對話框詢問設定前景/背景顏色,以及是否反轉黑白。 -
Convert to Mask 轉為遮罩: 根據目前的閾值設定將影像轉成二值圖。若未設定閾值,則會自動計算。預設輸出為「反轉 LUT」(白為 0、黑為 255),除非在
Process > Binary > Options中勾選了 Black Background。
侵蝕與膨脹(Erode & Dilate)
-
Erode 侵蝕: 從黑色物件邊緣移除像素,相當於縮小物件。可用來去除尖角、毛刺或細小突出。對灰階影像可使用
Process > Filters > Minimum模擬。 -
Dilate 膨脹: 向黑色物件邊緣加入像素,相當於擴大物件。可填補小孔或斷裂。對灰階影像可使用
Process > Filters > Maximum模擬。
組合操作
-
Open 開啟: 先侵蝕再膨脹。可移除小雜訊、斷開細連線。適合清除背景雜點而不影響主體。
-
Close 關閉: 先膨脹再侵蝕。可填補小孔洞、連接相近物體。適合使主體更為連貫。
其他操作
-
Skeletonize 骨架化: 持續移除物體邊緣像素,直到只剩單像素寬的骨架。用於分析結構拓撲(如細胞通路)。
-
Outline 描邊: 對物件產生單像素寬邊框。可視為邊緣檢測的一種形式。
-
Distance Map 距離變換: 計算每個前景像素與最近背景像素的歐式距離,結果為灰階圖,產生Euclidian distance map (EDM)。適合用於分析粒子間距或後續分割。
-
Ultimate Points 終極點: 對距離圖找出每個粒子內最大內切圓的中心,灰階值代表半徑。可作為分割粒子依據。產生ultimate eroded points (UEPs)。
-
Watershed 分水嶺分割: 自動分離接觸或重疊的粒子。流程包含建立距離圖、找終極點,然後從終極點開始膨脹直到互相接觸為止。適用於圓形、不重疊太多的粒子分離。
-
Voronoi 沃羅諾伊分割: 依據與最近兩個粒子的邊界距離,為每個粒子建立一個區域。適合做為粒子領域劃分(Voronoi tessellation)。
設定選項(Options)
透過 Process > Binary > Options... 可調整以下參數:
-
Iterations(次數): 設定侵蝕、膨脹、開啟、關閉等操作的重複次數。
-
Count(鄰近像素數): 決定侵蝕/膨脹時像素被加入/移除所需的鄰近像素數。
-
Black Background: 勾選此選項代表背景為黑,物件為白。這會影響大多數形態操作與距離圖的計算。
可用下列方式設定:
// Plugin
Prefs.blackBackground = true;
// Macro
setOption("black background", true);
-
Pad Edges when Eroding: 勾選時,侵蝕操作不會作用於影像邊緣(避免邊界損失)。
-
EDM Output(距離圖輸出格式): 設定 Distance Map、Ultimate Points、Voronoi 等輸出的格式:
-
"Overwrite":覆蓋原圖(8-bit)
-
"8-bit" / "16-bit" / "32-bit":輸出為新的影像,32-bit 為 subpixel 精度。
-
實作
幾何圖形
執行以下Macro,進行各種二值化操作,觀察這些圖形的變化
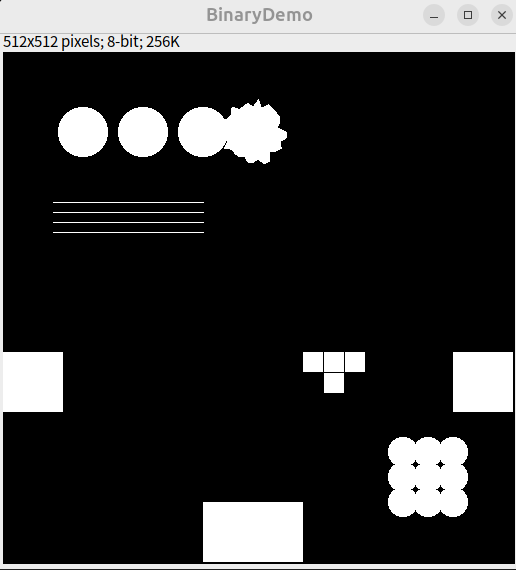
// 建立空白影像
newImage("BinaryDemo", "8-bit black", 512, 512, 1);
setForegroundColor(255, 255, 255);
// ---------- 粗圓 + 毛刺 ----------
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
x = 80 + i * 60;
y = 80;
r = 25;
makeOval(x - r, y - r, r * 2, r * 2);
fill();
}
// 毛刺圓形
centerX = 250;
centerY = 80;
nPoints = 36;
xPoints = newArray(nPoints);
yPoints = newArray(nPoints);
for (i = 0; i < nPoints; i++) {
angle = 2 * PI * i / nPoints;
r = 25 + random() * 10;
xPoints[i] = centerX + r * cos(angle);
yPoints[i] = centerY + r * sin(angle);
}
makeSelection("polygon", xPoints, yPoints); fill();
// ---------- 細線 ----------
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
y = 150 + i * 10;
makeLine(50, y, 200, y);
run("Draw", "slice");
}
// ---------- 貼邊形狀 ----------
makeRectangle(0, 300, 60, 60); fill();
makeRectangle(450, 300, 60, 60); fill();
makeRectangle(200, 450, 100, 60); fill();
// ---------- 破碎物件 ----------
setColor(255, 255, 255);
makeRectangle(300, 300, 20, 20); fill();
makeRectangle(321, 300, 20, 20); fill();
makeRectangle(342, 300, 20, 20); fill();
makeRectangle(321, 321, 20, 20); fill();
// ---------- 密集群圓 ----------
x0 = 400;
y0 = 400;
r = 15;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
dx = x0 + i * 25;
dy = y0 + j * 25;
makeOval(dx - r, dy - r, r * 2, r * 2);
fill();
}
}
// 二值化
run("Make Binary");
細胞分佈
執行以下macro,產生三張圖片,模擬不同的粒子分佈,試試看執行Voronoi分隔。
// 參數設定
width = 512;
height = 512;
pointRadius = 3;
// 建立空白影像
newImage("Multi-Pattern Particles", "8-bit black", width, height, 1);
setForegroundColor(255, 255, 255);
// -------------------- 區域1:隨機分佈 --------------------
nRandom = 50;
for (i = 0; i < nRandom; i++) {
x = random()*160 + 10; // 區域X: [10,170]
y = random()*160 + 10; // 區域Y: [10,170]
makeOval(x - pointRadius, y - pointRadius, pointRadius*2, pointRadius*2);
fill();
}
// -------------------- 區域2:密集群聚 --------------------
nClusters = 3;
pointsPerCluster = 20;
for (c = 0; c < nClusters; c++) {
cx = 200 + c * 30 + random()*10; // 區域X: 約在 200-300
cy = 60 + random()*60;
for (i = 0; i < pointsPerCluster; i++) {
dx = random()*20 - 10;
dy = random()*20 - 10;
x = cx + dx;
y = cy + dy;
makeOval(x - pointRadius, y - pointRadius, pointRadius*2, pointRadius*2);
fill();
}
}
// -------------------- 區域3:規則排列 --------------------
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
x = 350 + i * 20;
y = 50 + j * 20;
makeOval(x - pointRadius, y - pointRadius, pointRadius*2, pointRadius*2);
fill();
}
}
// 完成後進行二值化
run("Make Binary");
Top-hat 濾波
Top-hat 濾波是一種基於形態學開運算的背景校正與特徵增強方法,方法是:原圖 - 開運算結果,突顯比結構元素小的亮特徵(常用)。
主要應用
- 背景分離/校正:移除不均勻照明、背景雜訊,讓前景物體更明顯。
- 對比增強:提升小型亮(或暗)特徵的對比度。
- 特徵提取:強調影像中特定大小的細節,便於後續分割或量測。
ImageJ 操作
Process > Filters > Top Hat...
結構元素半徑建議大於目標特徵,且小於背景變化尺度。
Macro 範例
run("Blobs (25K)");
run("Invert LUT");
run("Duplicate...", "title=topHat50");
run("Top Hat...", "radius=50");